Dora: Sampling and Benchmarking for 3D Shape Variational Auto-Encoders

Table Of Content
- What is Dora?
- Dora 3D Shape AI Tool:
- The Challenge with Current VAEs
- How Dora Improves 3D Modeling
- Examples of Dora’s Capabilities
- Example 1: Snowman
- Example 2: Wooden Board
- Example 3: Complex Character Design
- Example 4: Person Holding a Beer
- Example 5: Dragon
- Example 6: Mecha Robot
- Example 7: Bulldog’s Face
- Example 8: Cat Gundam Creature
- Practical Applications of Dora
- Real-Time Processing
- Availability of Dora
In this article, I’ll walk you through an exciting AI tool called Dora, which is capable of generating highly accurate 3D models from just a single photo. This technology is not only fascinating but also incredibly practical for anyone working in 3D modeling, animation, or game development. Here, we get into the details of how Dora works, its unique features, and some impressive examples of its capabilities.
What is Dora?
Dora is a variational auto-encoder (VAE), a type of AI model that specializes in compressing and decompressing data. If you’ve worked with tools like Comfy UI, Stable Diffusion, or Flux, you might already be familiar with VAEs. In simple terms, a VAE takes complex data, compresses it into a simpler form, and then reconstructs it back into its original format.
In the case of Dora, this process is applied to 3D shapes. It compresses complex 3D shapes into simplified data and then reconstructs them back into detailed 3D models. This makes Dora a powerful tool for generating 3D models from minimal input, such as a single image.
Dora 3D Shape AI Tool:
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Name | Dora |
| Category | 3D Shape Variational Auto-Encoder (VAE) |
| GitHub Link | GitHub Page |
| Project Link | Official Project Document |
| Official YouTube Video | Dora Youtube |
The Challenge with Current VAEs
Current VAEs used for 3D modeling rely on a method called uniform point sampling. While this approach works, it often leads to a loss of detail in the reconstructed 3D shapes. As a result, the final models might not look as good as the original ones.
How Dora Improves 3D Modeling
Dora introduces a new approach called sharp edge sampling, which addresses the limitations of uniform point sampling. This method focuses on identifying and prioritizing the most important parts of a 3D shape, such as sharp edges and corners. By doing so, Dora preserves more details and generates higher-quality 3D models.
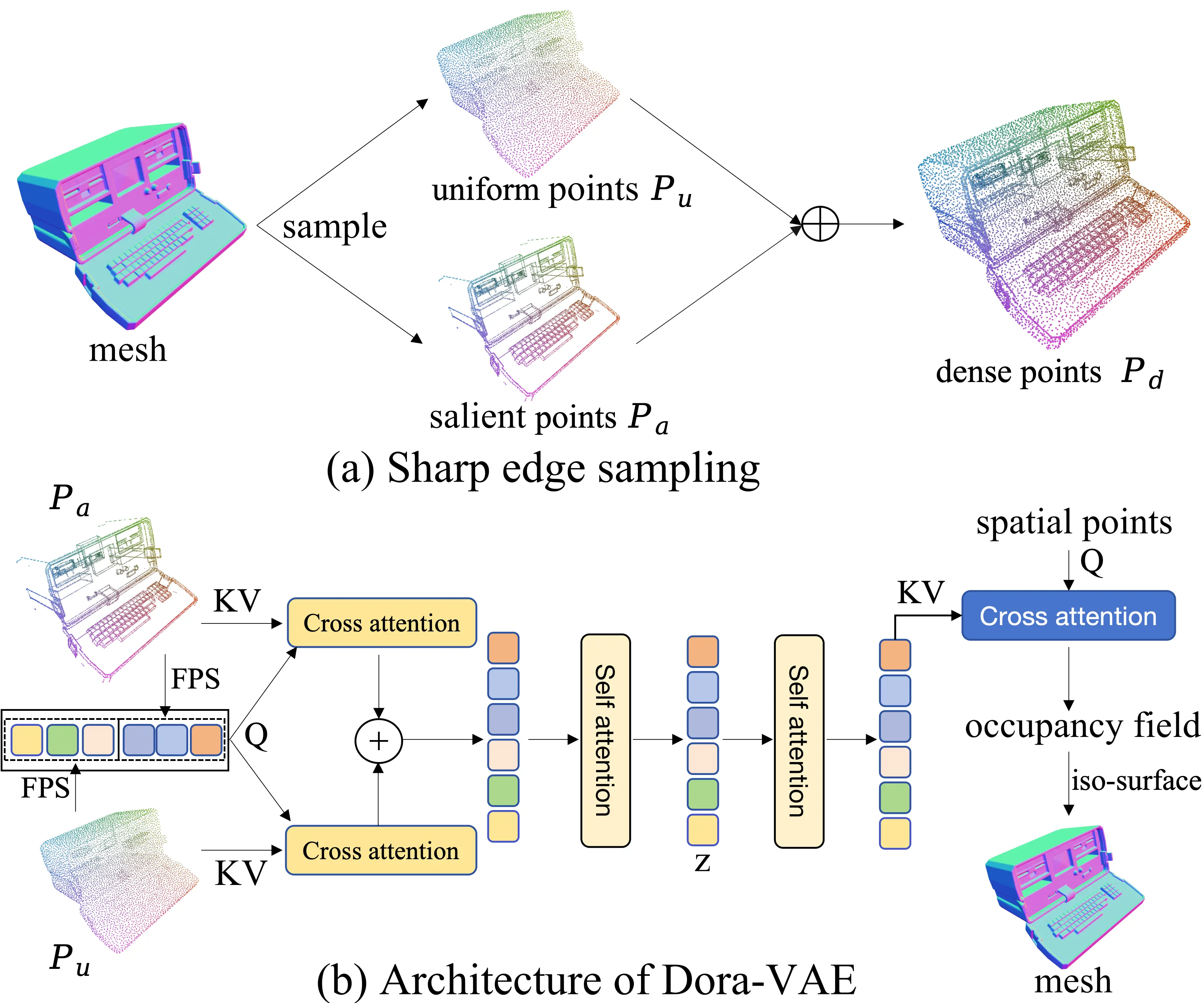
Examples of Dora’s Capabilities
To give you a better understanding of Dora’s capabilities, let’s look at some examples of 3D models generated by this AI tool.
Example 1: Snowman
- Input Image: A simple image of a snowman.
- Output: A detailed 3D model of the snowman, including the backside, which the AI had to infer since it wasn’t visible in the original image.
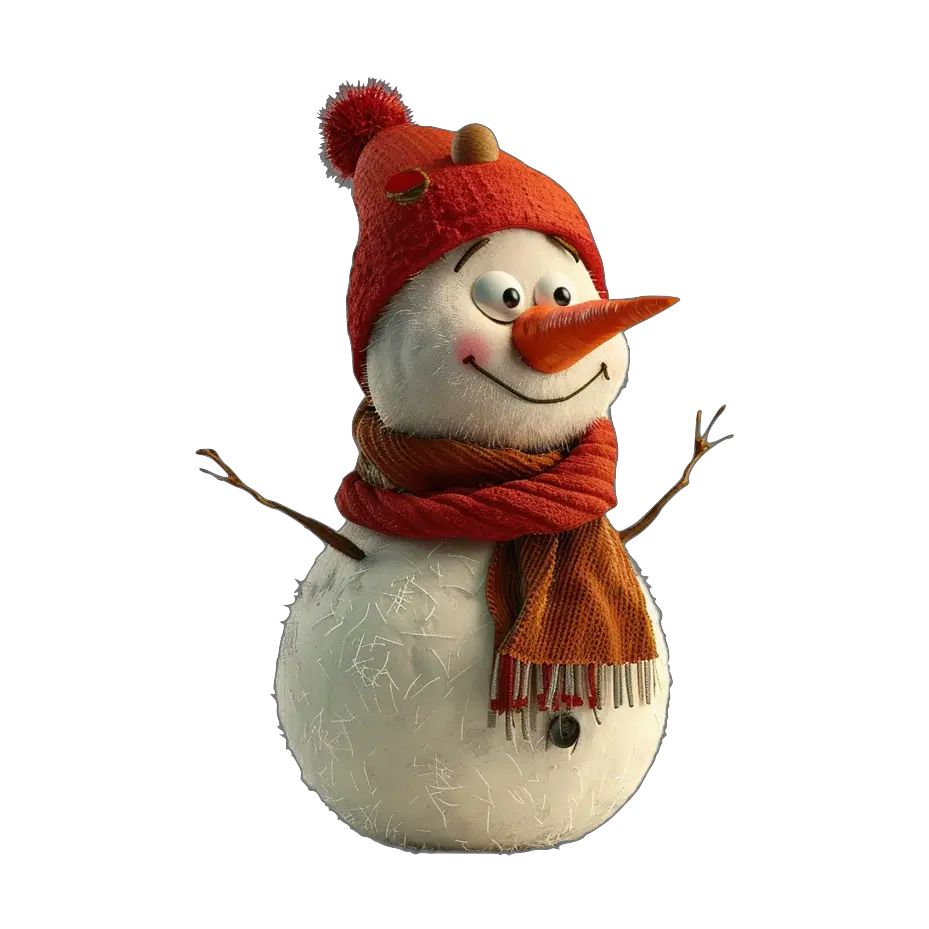

This example demonstrates how Dora can accurately guess and reconstruct parts of an object that aren’t visible in the input image.
Example 2: Wooden Board
- Input Image: An image of a wooden board.
- Output: A 3D model of the wooden board, complete with the backside accurately reconstructed.
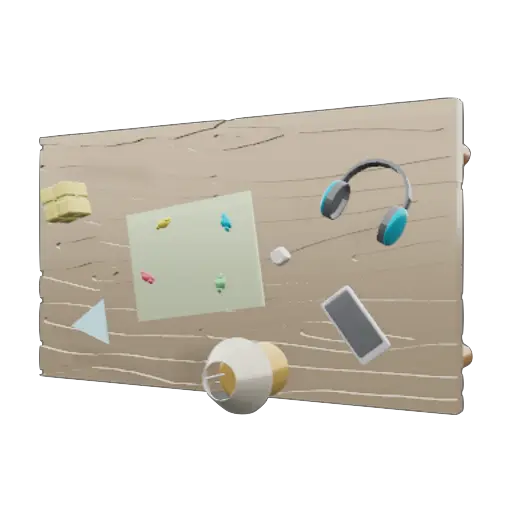

Again, Dora successfully inferred the hidden parts of the object, showcasing its ability to handle complex reconstructions.
Example 3: Complex Character Design
- Input Image: An image of a highly detailed character with intricate designs on their coat.
- Output: A 3D model that captures all the complex details, including badges and patterns on the coat.
This example highlights Dora’s ability to handle intricate designs and produce high-quality 3D models.
Example 4: Person Holding a Beer
- Input Image: An image of a person holding a glass of beer.
- Output: A 3D model that accurately replicates the person’s pose and the details of the beer glass.
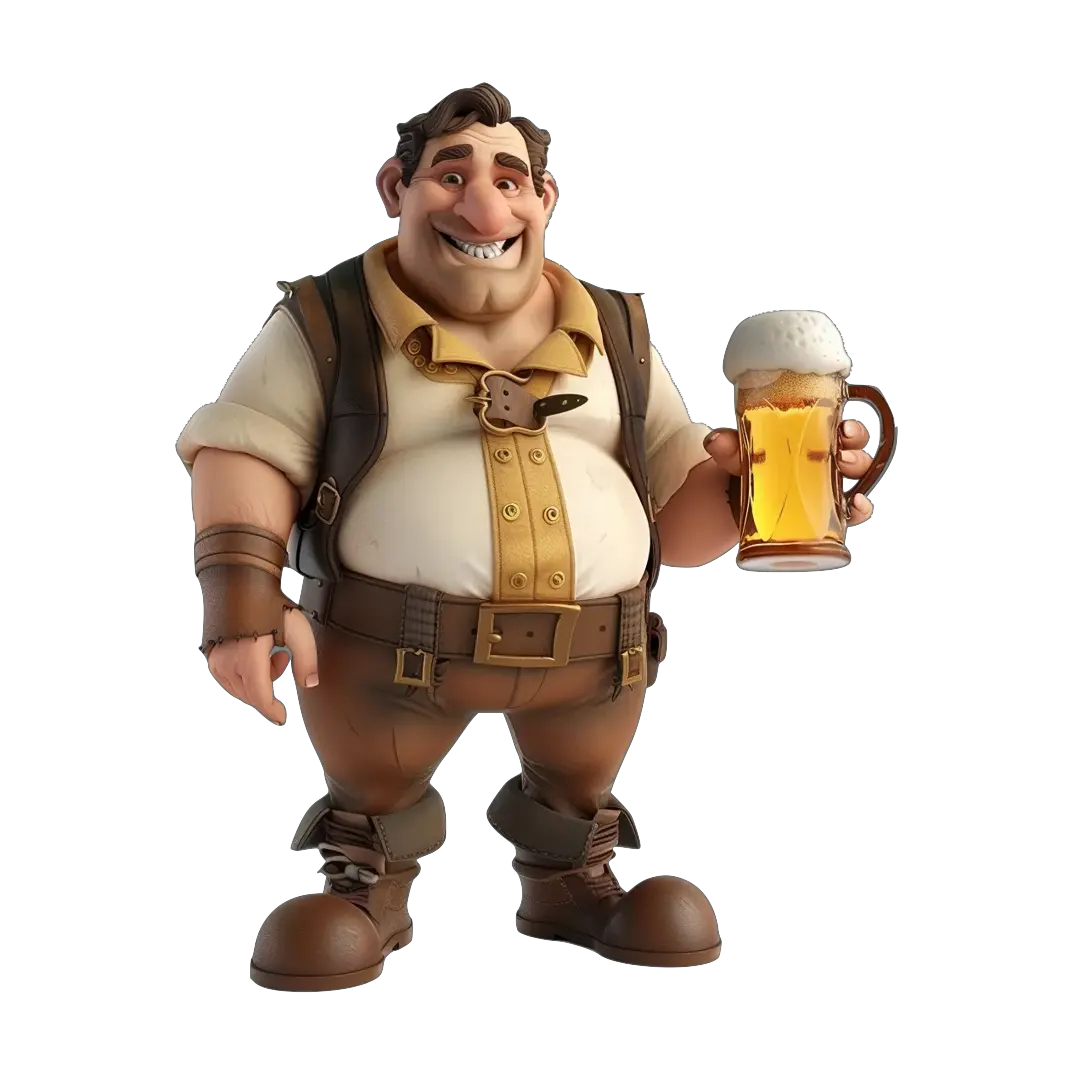

This demonstrates Dora’s capability to handle complex poses and objects within a single image.
Example 5: Dragon
- Input Image: An image of a dragon.
- Output: A highly detailed 3D model of the dragon, capturing all its intricate features.
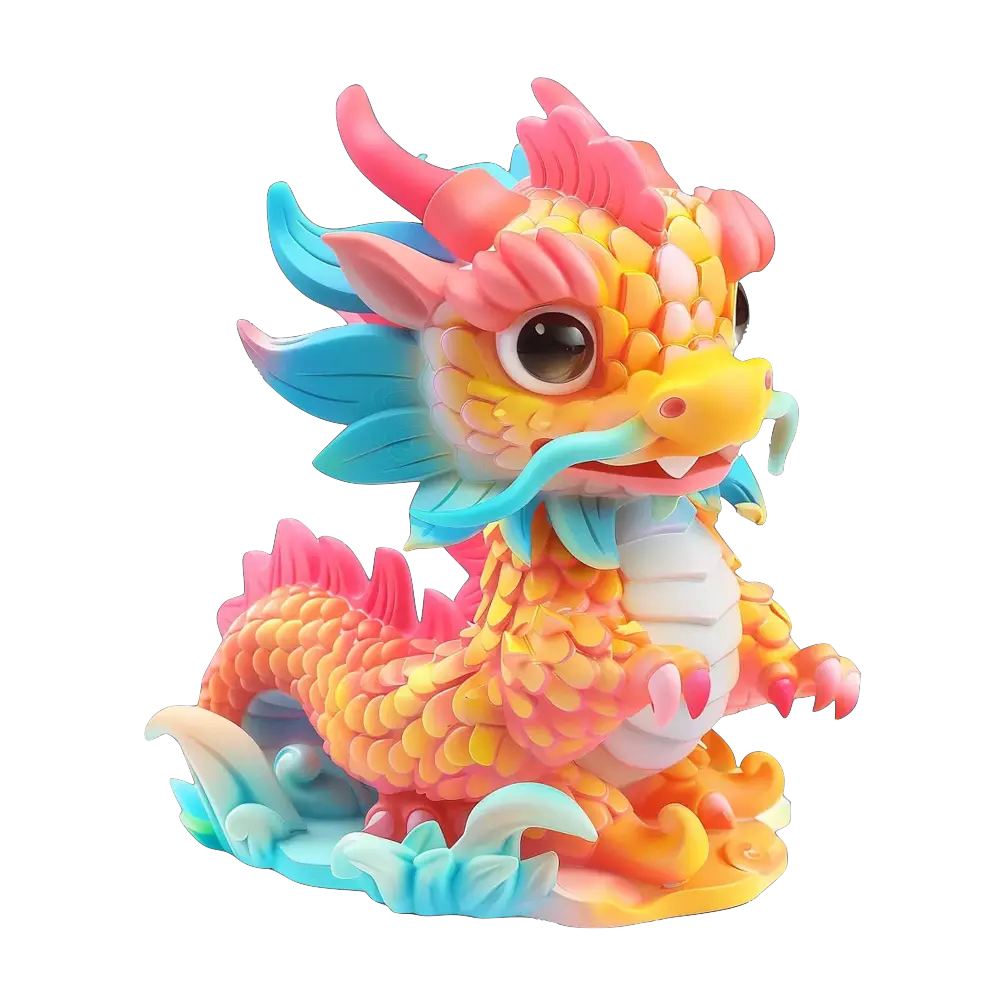

Dora’s ability to handle such a complex and detailed design is truly impressive.
Example 6: Mecha Robot
- Input Image: An image of a highly detailed Mecha Robot.
- Output: A 3D model that accurately replicates the robot’s intricate design.
This example shows how Dora can generate high-quality 3D models even from highly detailed and complex input images.
Example 7: Bulldog’s Face
- Input Image: An image of a bulldog’s face.
- Output: A 3D model that captures the wrinkles and facial features of the bulldog with remarkable accuracy.
Handling the fine details of a bulldog’s face is no easy task, but Dora manages it exceptionally well.
Example 8: Cat Gundam Creature
- Input Image: An image of a Cat Gundam creature.
- Output: A 3D model that replicates the complex and tricky design of the creature.
This example further emphasizes Dora’s ability to handle unique and challenging designs.
Practical Applications of Dora
One of the most exciting aspects of Dora is that the 3D models it generates are ready to use in modern 3D engines like Unity. This means you can take a single image, generate a 3D model using Dora, and immediately use it in real-time applications such as games or animations.
Real-Time Processing
Dora is also highly compute-efficient. According to the developers, Dora achieves comparable reconstruction quality to state-of-the-art methods while requiring a latent space at least eight times smaller. This means Dora can generate high-quality 3D shapes using fewer computational resources, making it a practical tool for real-time applications.
Availability of Dora
At the time of writing, the code for Dora is not yet available, but the developers have indicated that it will be open-sourced soon. I’ll provide a link to the page where you can find additional examples and updates on the release.
In conclusion, Dora represents a significant step forward in 3D modeling technology. Its ability to generate high-quality 3D models from a single image, combined with its computational efficiency, makes it a valuable tool for a wide range of applications.

