GenHMR: Generative Human Mesh Recovery

Table Of Content
- What is GenHMR?
- GenHMR Overview
- Examples of GenHMR in Action
- High-Action Scenes
- Chaotic War Scenes
- Race Footage
- How GenHMR Works
- Stage 1: Uncertainty-Guided Sampling
- Stage 2: 2D Pose-Guided Refinement
- GenHMR: Generative Human Mesh Recovery Explained
- **Training Phase**
- **How It Works (Inference)**
- **Why It’s Better**
- **Results on Hard Poses**
- **Refinement Process**
- **More Challenging Poses**
- Limitations and Flaws
- Misaligned Poses
- Wide-Angle Shots
- Availability of GenHMR
- The Future of Motion Capture
- Conclusion
In this article, I’ll walk you through an exciting AI tool called GenHMR, which stands for Generative Human Mesh Recovery. This technology is designed to analyze videos and detect the 3D poses and models of people within them. Before diving into the technical details, let’s take a look at some impressive examples of what GenHMR can do.
What is GenHMR?
GenHMR (Generative Human Mesh Recovery) is an AI tool that analyzes videos to detect and generate 3D poses and models of people. It works in two stages: first, it creates multiple possible 3D poses and selects the most likely one, and second, it refines the pose to better match the original video.
While highly accurate in many scenarios, it has some limitations, such as misaligned poses in complex movements or wide-angle shots. GenHMR has the potential to replace traditional motion capture methods, eliminating the need for marker suits.
GenHMR Overview
| Detail | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | GenHMR |
| Purpose | Detects and generates 3D human poses and models from video footage. |
| GitHub Page | GenHMR GitHub Page |
| Official Paper | GenHMR Paper on arXiv |
Examples of GenHMR in Action
High-Action Scenes
One of the standout examples involves a high-action scene where characters are running and performing acrobatic moves across rooftops. Despite the fast-paced and dynamic movements, GenHMR accurately predicts the poses of these characters.
The AI manages to keep up with the rapid changes in their positions, showcasing its ability to handle complex scenarios.
Chaotic War Scenes
Another example features a chaotic war scene with multiple people running around, explosions occurring, and general mayhem. Even in such a disorderly environment, GenHMR successfully detects the poses of most characters with high accuracy.
This demonstrates its robustness in handling crowded and unpredictable situations.
Race Footage
In a third example, GenHMR is applied to footage of a race. Here, the AI detects the poses of all the runners with remarkable precision. This further highlights its capability to analyze and interpret human movements in various contexts.
From these examples, it’s clear that GenHMR excels at detecting the poses and 3D models of multiple humans in a video, even in challenging scenarios.
How GenHMR Works
GenHMR operates in two main stages: Uncertainty-Guided Sampling and 2D Pose-Guided Refinement. Let’s break down each stage to understand how the system functions.
Stage 1: Uncertainty-Guided Sampling
In the first stage, GenHMR generates multiple possible 3D poses for all the people in the video. It then evaluates these poses and selects the most likely one based on the input image. This step ensures that the initial 3D model is as accurate as possible before moving on to the next stage.
Stage 2: 2D Pose-Guided Refinement
The second stage focuses on refining the generated pose and 3D model to better align with the original image or video. This refinement process enhances the accuracy of the final output, making it more consistent with the actual movements and positions of the people in the video.
GenHMR: Generative Human Mesh Recovery Explained
Training Phase
GenHMR has two main parts:
- Pose Tokenizer: Turns 3D human poses into a series of simplified codes (tokens).
- Image-Conditioned Masked Transformer: Uses these tokens and the input image to predict the most likely 3D poses.
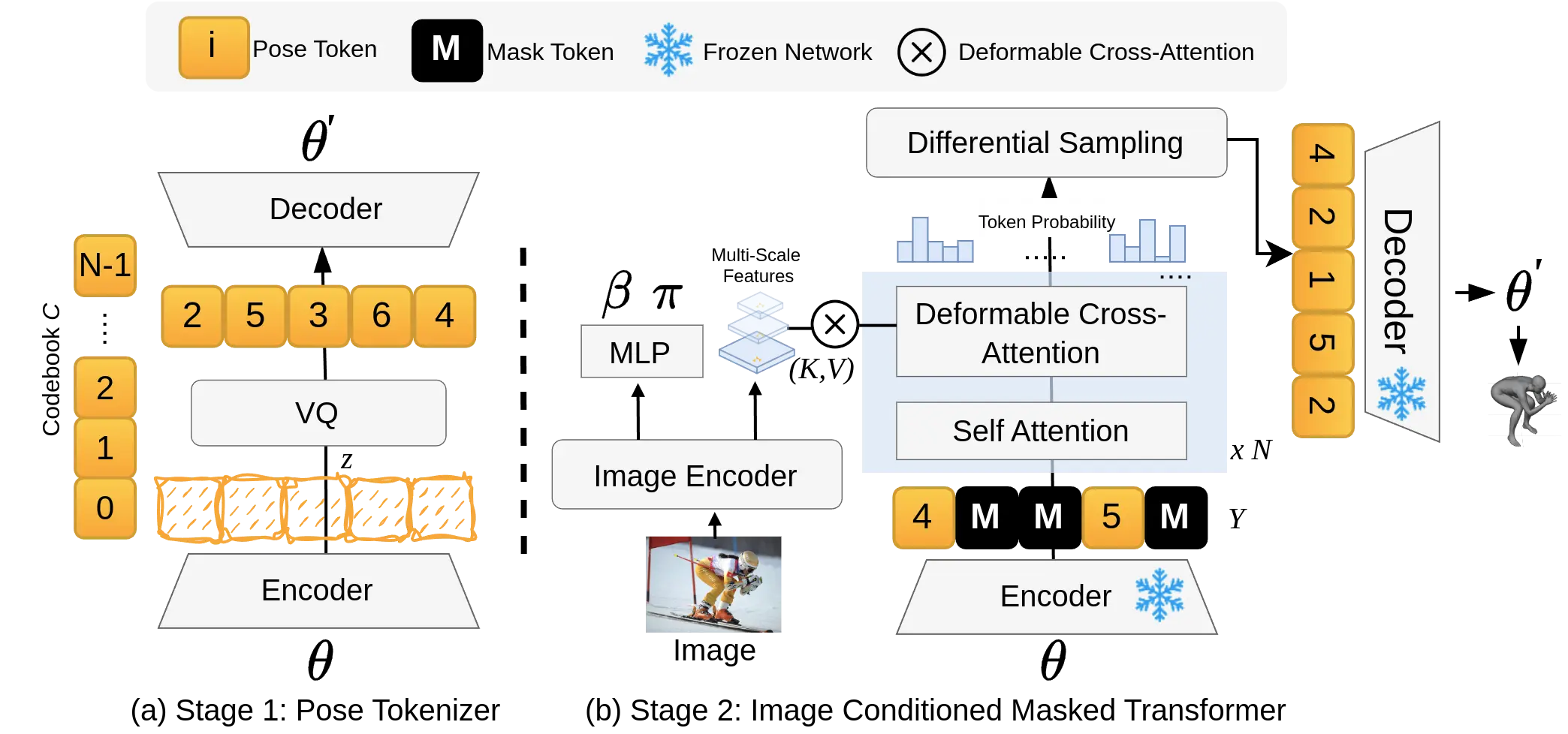
How It Works (Inference)
- Uncertainty-Guided Sampling: Picks the best 3D pose tokens based on their confidence.
- 2D Pose-Guided Refinement: Fine-tunes the 3D pose to match the 2D image better, making it more accurate.
Why It’s Better
Other methods like HMR2.0 and TokenHMR struggle with tricky poses or unclear situations. GenHMR fixes this by reducing errors in turning 2D images into 3D poses, making it more reliable in complex cases.
Results on Hard Poses
GenHMR works well even on difficult poses, as shown in tests on the LSP dataset. It starts with a rough 3D pose and improves it step by step.
Refinement Process
The 2D Pose-Guided Refinement fixes errors in the 3D pose over several steps. By the 10th step, most mistakes are corrected, making the final result much more accurate.
More Challenging Poses
GenHMR also handles very complex poses well, showing its strength in tough situations.
In short, GenHMR is a smart tool that turns 2D images into accurate 3D human poses, even in tricky or unclear scenarios.
Limitations and Flaws
While GenHMR is highly effective, it’s not without its flaws. Here are some examples where the tool struggles:
Misaligned Poses
In certain video frames, the generated pose doesn’t align perfectly with the person’s arms and legs. For instance, in some gymnastics footage, the toes aren’t pointing in the correct direction. This indicates that the tool may have difficulty interpreting specific body parts in certain poses.
Wide-Angle Shots
GenHMR also faces challenges with wide-angle shots. In one example, the size of a person’s hands and feet doesn’t appear correct in the generated model. This suggests that the tool may struggle with perspective distortions caused by wide-angle lenses.

Availability of GenHMR
Unfortunately, as of now, there is no GitHub or Hugging Face link available for GenHMR. This means the code hasn’t been released to the public yet. However, the examples and demonstrations we’ve seen so far indicate that this tool has the potential to significantly impact motion capture technologies.
The Future of Motion Capture
GenHMR has the potential to replace traditional motion capture methods. With this technology, there’s no longer a need for actors to wear suits with markers or go through the tedious process of traditional motion capture. Instead, GenHMR can generate accurate 3D human poses directly from video footage, making the process faster and more efficient.
Conclusion
GenHMR is a fascinating tool that showcases the capabilities of AI in analyzing and interpreting human movements. While it still has some limitations, its potential applications in animation, gaming, and other fields.
Related Posts

3DTrajMaster: A Step-by-Step Guide to Video Motion Control
Browser Use is an AI-powered browser automation framework that lets AI agents control your browser to automate web tasks like scraping, form filling, and website interactions.

Caracal AI: Free Tool for Handwritten Text Recognition, Extract text from Images
Caracal is a text recognition project that has been widely cloned and fine-tuned by users for specific purposes. The project leverages advanced technology for text recognition tasks, as highlighted in the provided transcript snippet.

Browser-Use Free AI Agent: Now AI Can control your Web Browser
Browser Use is an AI-powered browser automation framework that lets AI agents control your browser to automate web tasks like scraping, form filling, and website interactions.
